xrf spectrometer working principle|how does xrf analysis work : Big box store Energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence (EDXRF), commonly referred to as XRF, is a fast, nondestructive method to measure the elemental composition of a . Resultado da Líder em Software de iGaming Seu Cassino Online entregue em 24h Construa seu novo negócio de sucesso, e tenha um cassino online com .
{plog:ftitle_list}
OmniROM is our Android custom ROM variant, feature-packed but always with stability as #1 priority in mind. Based on the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) and enriched by .
xrf analyzer how it works
Energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence (EDXRF), commonly referred to as XRF, is a fast, nondestructive method to measure the elemental composition of a .This booklet gives a general introduction to X-Ray fluorescence (XRF) spectrometry and XRF analysis. It explains simply how a spectrometer works and how XRF analysis is done. It is intended for people new to the field of XRF analysis. Difficult mathematical equations are avoided and the booklet requires only a basicXRF is an acronym for X-ray fluorescence, a process whereby electrons are displaced from their atomic orbital positions, releasing a burst of energy characteristic of a specific element. . CTX BenchTop XRF spectrometer. .Fundamental Principles Introduction to X-Ray Fluorescence Analysis (XRF) 2 DOC-M84-EXX001 V8 – 10.2016 Bohr's Atomic Model Bohr's atomic model describes the structure of an atom as an atomic nucleus surrounded by electron
X-ray fluorescence principles including EDXRF and WDXRF, . webinars, and other resources below to see how you can put X-ray fluorescence (XRF) to work for your specific application. Discover the XRF Academy. XRF documents. Read our brochures, eBooks, and flyers to learn more about XRF and its uses in diverse applications. . ARL PERFORM'X .Americium (95) is the element with the highest atomic number covered. XRF provides detection limits at the sub-ppm level for many elements; it can also measure concentrations of up to 100% easily and simultaneously. X-ray Fluorescence Analyzers. SPECTRO is a world leader in the manufacture of energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometers.
tear test for dry eyes
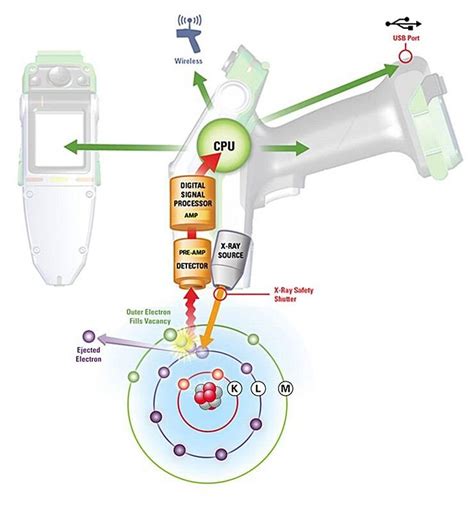
14.6 X-ray fluorescence analysis. X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy is a method that allows rapid and multielemental qualitative and quantitative analysis of recycled nanoparticles [9]. The method is nondestructive, it has high precision and accuracy, and detection can be achieved at the level of parts per million or a few tenths of a percent.The current X-ray fluorescence spectrometer is equipped with crystals with different interplanar spacings to analyze elements in different ranges. The above-mentioned spectroscopic system relies on the rotation of the spectroscopic crystal and the detector to make the characteristic X-rays of different wavelengths sequentially detected. “Ownership” of XRF Within Academia. Although XRF is a physical phenomena involving the interaction of X-rays with matter, most of the applications of XRF are in areas outside of physics (chemistry, environmental sciences, food and product quality monitoring, etc.); Although XRF requires specialized knowledge in chemistry (spectral interpretation, calibration, . This video best details and explains the fundamentals of an XRF’s Principle of Operation.. A prepared sample specimen is excited by the radiation of an X-Ray. This causes a electrons from the inner electron shells to get knocked-off. Electrons from outer electron shells drop-in to fill the resultant voids emitting a fluorescence radiation characteristic in its energy .
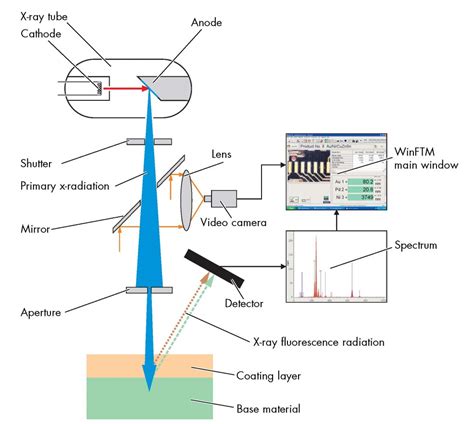
Sequential X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer An evolutive platform The Thermo Scientific™ ARL™ PERFORM’X wavelength-dispersive X-ray fluorescence (WDXRF) spectrometer presents an advanced platform for rapid and precise analysis of up to 90 elements in nearly any solid or liquid sample. Advantages over other analytical techniques are: Principle of X-Ray Spectroscopy. XRF works on methods involving interactions between electron beams and x-rays with samples. . Working of X-Ray Spectroscopy . An XRF spectrometer works because if a sample is illuminated by an intense X-ray beam, known as the incident beam, some of the energy is scattered, but some is also absorbed within the .
A spectrometer consists of several components. A USB spectrometer is the most common type of spectrometer. They take light, separate it by wavelength and create a spectrum which shows the relative intensity of these separate wavelengths. Spectrometers have a wide range of applications and uses. What is X-ray Fluorescence? X-ray fluorescence is an analytical technique that can be used to determine the chemical composition of a wide variety of sample types including solids, liquids, slurries and loose powders. XRF is also used to determine the thickness and composition of layers and coatings.Basic principles X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the phenomenon in which X-rays of energy characteristic of an element are emitted following excitation of the test material by energetic X-rays. X-ray fluorescence occurs when an atom is excited by a process of sufficient energy to eject an electron from an inner orbital shell.Introduction X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) is a nondestructive method for the elemental analysis of solids and liquids. The sample is irradiated by an intense x-ray beam, which causes the emission of fluorescent x-rays. The emitted x-rays can either be detected using energy dispersive or wavelength dispersive detector. Either the energies or wavelengths of the emitted x-rays are .
Exciting samples with primary X-rays and acquiring the resulting X-ray fluorescence signals enables chemists to develop an accurate spectrum of sample composition. There are numerous ways this can be carried out, though the two primary techniques are known as energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence (EDXRF) and wavelength dispersive X-ray .
The XRF spectrometer measures the energy (ΔE) and intensity (I) of the X-ray fluorescence signal emitted from a sample by irradiation of X-rays, and thus, an XRF spectrum is obtained. The XRF spectrometer is composed of an X-ray source, sample chamber, X-ray detector, and electronic devices for signal processing, amplification, counting, and .
The first post in this series, Laboratory-based XRF vs. Handheld XRF: What’s the Difference? explained that handheld XRF analyzers are designed for situations where immediate feedback is needed, whereas lab-based XRF analysis has a wider analytical range and is suited for more applications. The two primary types of lab-based XRF systems are Energy Dispersive . The traditional use of X-ray fluorescence analysis (XRF) has its roots in geology. Solid samples were the first sample types analyzed by X-rays. Over the yea. X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is a technique which non-destructively analyses a material to identify the elements that make it up [1].A material bombarded with high-energy X-rays absorbs it and emits .
x ray fluorescence thickness measurement
Wavelength Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry (WDXRF) The WDXRF spectrometers from Bruker are known for its unrivalled accuracy, precision and reliability. Based on state-of-the-art and robust technology Bruker spectrometers are established in all kinds of industrial applications, such as cement, polymers, refineries, mining, and . Data obtained from the micro-X-Ray fluorescence–energy dispersive spectrometer (μ-XRF) analyses of the same sample suite concur with the alteration and mineralization characteristics identified .
2 XRF Fundamentals Principle of XRF The effect of X-ray fluorescence is based on the excitation of atoms in the sample. Unlike optical spectroscopy, the excitation involves interaction with the inner shell electrons rather than valence electrons as indicated in the image of the Bohr model of the atom below. The process of X-ray Fluorescence beginsX-ray Fluorescence (XRF) is an analytical technique that uses the interaction of X-rays with a material to determine its elemental composition. XRF is suitable for solids, liquids and powders, and in most circumstances is non-destructive. . An introduction to modern X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) micro-spectroscopy, principles of XRF and its micro . X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectrometry is a non-destructive analytical technique used to obtain elemental information from different types of materials.. It is employed in many industries and applications including: cement production, glass production, mining, mineral beneficiation, iron, steel and non-ferrous metals, petroleum and petrochemicals, polymers and .EDXRF (energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence) is a non-destructive analytical technique that provides quick qualitative and quantitative elemental analysis of a wide range of matrices, from low ppm to high weight percent concentrations. . The excess energy is emitted as an X-ray, and the spectrometer counts and measures the energies of these X .
what is a xrf analyzer
how to read xrf results
Resultado da 4 de jul. de 2023 · Edição 2023 tem distribuição recorde. copa do brasil. TIMES. Série A. Série B. Europa. Premiação da Copa do Brasil 2023: veja valores de cada fase. Quartas de final da competição começam nesta terça-feira, e classificação vale R$ 9 milhões. Edição 2023 tem distribuição .
xrf spectrometer working principle|how does xrf analysis work